Understanding the Basics – Why Process Integration Matters
In today’s fast-paced business environment, ensuring that all your systems and processes work together seamlessly is essential for staying competitive. This is where process integration comes into play. At its core, process integration connects different systems, departments, and workflows, enabling them to communicate and work together efficiently. This reduces redundant tasks, eliminates bottlenecks, and helps businesses make better decisions faster.
Think of a large company with multiple departments—finance, sales, human resources, and operations. Each department likely uses its own software and tools to handle specific tasks. Without integration, these systems operate in silos, making it difficult to share information and keep everything aligned. This can lead to delays, miscommunication, and even costly errors. But when systems are integrated, everything flows smoothly. Data can move from one department to another without manual input, processes are streamlined, and employees can focus on more valuable work.
Key Terms You Should Know
Before diving deeper into how process integration works, let’s cover a few essential terms:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): An ERP system is a software platform that helps businesses manage core processes in one place. This includes everything from accounting to supply chain management. ERP systems rely on process integration to bring together data from different departments, ensuring that everyone has access to up-to-date information.
- API (Application Programming Interface): APIs allow different software systems to communicate with each other. Think of it as a bridge between two systems that lets them share data and functions. For example, a company’s CRM system might use an API to pull customer data from their finance software.
- Middleware: Middleware is the glue that connects different software applications. It enables disparate systems to communicate and share information, without requiring them to be directly linked. Middleware is particularly useful in complex IT environments where multiple tools are in use, as it simplifies the integration process.
- Data-Sharing Protocols: These are the rules and formats that systems use to exchange data. Common protocols like XML or JSON help ensure that data is shared in a way that both systems can understand, regardless of how different they are.
How Integration Optimizes Workflows
When done right, process integration can transform the way your business operates. By connecting systems, you reduce the need for manual data entry and cut down on errors. For example, when a sales team closes a deal, the data automatically flows into the finance system for invoicing, and the operations team is notified to start the delivery process. This level of automation speeds up workflows and enhances productivity.
Also, integrated systems provide a holistic view of your business performance. Data from different departments can be analyzed together, enabling better decision-making. Instead of piecing together information from various sources, managers can quickly get insights and take action.
As we’ll explore in later sections, foundational technologies like APIs, middleware, and data-sharing protocols are critical for enabling this type of efficiency. But it’s not just about the technology—it’s about ensuring that your team has the right processes and strategies in place to make the most of integration efforts.
Tailoring Integration Solutions to Business Needs – Customizing the Right Approach for Your Organization
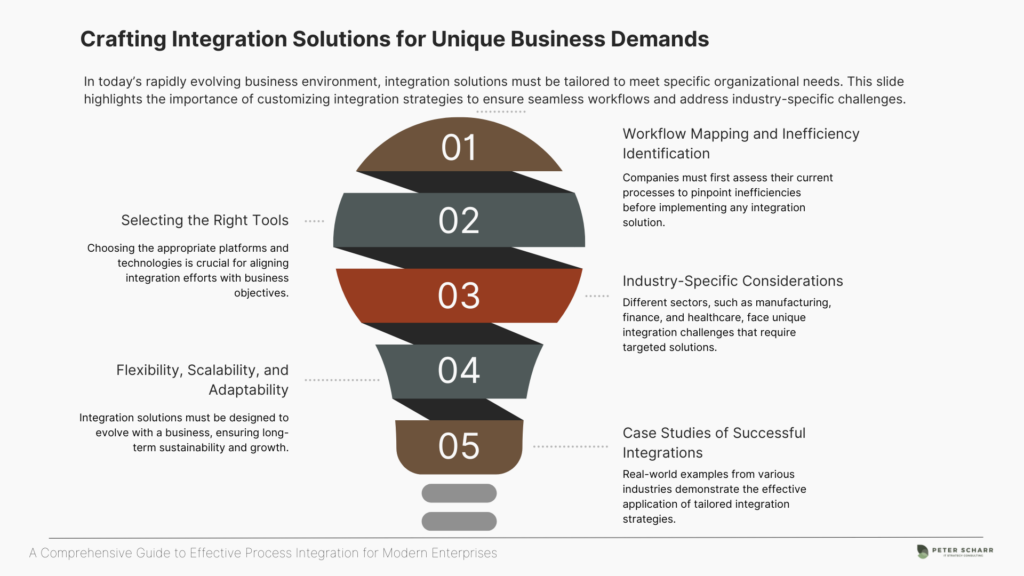
Every business is unique, and so are its needs when it comes to process integration. While the basic principles of integration—connecting systems, improving communication, and automating workflows—apply universally, the way these principles are implemented should be tailored to fit the specific goals, challenges, and scale of your organization. In this section, we’ll explore how businesses can map out their current workflows, pinpoint inefficiencies, and choose tools that align with their objectives. We’ll also look at real-world examples of successful integrations across different industries to illustrate how customization can make a big difference.
Mapping Your Current Workflows
Before diving into integration solutions, it’s crucial to understand how your current processes and systems function. This step is often overlooked, but it is essential for identifying inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement. By documenting your workflows, you create a clear picture of where manual tasks, data silos, or bottlenecks exist.
For example, in a manufacturing company, the production team might rely on a separate system from the inventory management team, leading to delays in reordering critical materials. By mapping out how information flows from one department to another, these gaps become evident, paving the way for a more seamless integration that can prevent costly delays and errors.
Identifying Inefficiencies
Once you’ve mapped your workflows, the next step is to identify areas where inefficiencies are slowing down your operations. Some common signs of inefficiency include:
- Manual data entry that duplicates effort across departments.
- Systems that don’t “talk” to each other, requiring employees to manually transfer information.
- Bottlenecks where tasks are delayed because of poor communication between systems or teams.
- Data silos that make it difficult to get a complete view of business operations.
By recognizing these trouble spots, you can start to envision how integration could streamline your processes, reduce errors, and save time. For example, integrating your ERP system with your customer relationship management (CRM) platform can help sales and finance departments access the same customer data, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing the chance of errors.
Selecting the Right Tools and Platforms
Now comes the fun part: choosing the tools and platforms that will help you achieve your integration goals. The right solution depends on the specific needs of your business, including the systems you already use, the scale of your operations, and the level of complexity involved.
There are many integration platforms available, each offering different features. Some companies opt for comprehensive middleware solutions that can connect multiple systems at once, while others might choose to use APIs to link specific software. As explained earlier (see: Key Terms You Should Know), APIs serve as bridges between systems, allowing them to exchange data easily and securely. Middleware, on the other hand, provides a more comprehensive solution for connecting multiple applications across different environments.
It’s also important to consider the scalability and flexibility of any integration tools you choose. As your business grows, you’ll need an integration solution that can grow with you, without requiring a complete overhaul. A flexible integration platform can adapt to changes in your processes, new technologies, and evolving business needs.
Industry-Specific Challenges
Different industries face different challenges when it comes to integration. For instance, in the healthcare sector, privacy and security concerns are paramount. Any integration efforts must comply with regulations like HIPAA, ensuring that sensitive patient information is handled securely. In contrast, manufacturing companies might prioritize real-time data accuracy to optimize supply chains and production efficiency.
In the finance industry, where data integrity and compliance are crucial, integration solutions must ensure that systems are not only connected but also adhere to strict reporting standards. Here, integrating transactional data across multiple platforms can help streamline financial reporting and reduce the risk of errors.
One example of successful integration in healthcare is the use of middleware platforms that connect electronic health records (EHR) with other medical systems, reducing the time doctors and nurses spend on administrative tasks and allowing them more time to focus on patient care. Similarly, in manufacturing, integrating systems like ERP and supply chain management tools can lead to real-time inventory tracking and more efficient production processes.
The Importance of Flexibility and Scalability
If there’s one thing to keep in mind, it’s that flexibility and scalability are key to any integration solution. As your business evolves, your processes will need to adapt. Whether it’s adding new software, expanding into new markets, or scaling up your operations, your integration strategy should be flexible enough to accommodate these changes without causing disruptions.
For example, cloud-based integration platforms offer a high degree of flexibility and scalability. Because they operate in the cloud, they can easily be expanded or modified as your needs change. This makes them ideal for growing businesses or those that operate in dynamic industries with constantly shifting requirements.
Ultimately, successful integration is about more than just connecting systems. It’s about creating a flexible, adaptable framework that can support your business
Overcoming Common Integration Challenges – Navigating Obstacles to Ensure Success
Even the best-laid integration plans can encounter obstacles along the way. From technological roadblocks to human resistance, modern enterprises face several challenges when trying to unite their systems. But don’t worry—these hurdles are not insurmountable! In this section, we’ll explore some of the most common challenges businesses face during process integration and offer actionable solutions to overcome them.
Technological Incompatibilities
One of the most frequent challenges in process integration is technological incompatibility. With businesses often using a mix of legacy systems, cloud-based tools, and third-party applications, getting everything to “talk” to each other can be difficult. Different software solutions might use incompatible formats or protocols, making it hard to share data seamlessly.
The solution? Invest in robust middleware or API-based solutions. As mentioned earlier (see: Key Terms You Should Know), middleware acts as a bridge between different systems, allowing them to communicate even if they weren’t initially designed to do so. API-driven integrations can also help connect disparate systems, enabling smoother data exchanges. Additionally, before choosing any new tools or platforms, ensure they are compatible with your existing infrastructure or provide easy integration options.
Data Silos
Many organizations struggle with data silos, where information is stored in separate systems or departments, making it difficult to access a unified view of the business. For example, sales might have different customer records than finance, or operations might not have access to real-time data from the supply chain. These silos create inefficiencies, duplicate efforts, and lead to inconsistent decision-making.
To break down these silos, a strong data-sharing strategy is essential. This involves integrating systems so that data flows freely across departments. An ERP system, as we discussed earlier, can help centralize data and ensure that all departments have access to the same information. Additionally, investing in data-sharing protocols like JSON or XML helps standardize how data is exchanged, promoting better collaboration between systems and teams.
Security Concerns
With greater integration comes a higher risk of security breaches. When multiple systems are connected, vulnerabilities in one system can potentially expose sensitive data across the entire organization. This is particularly critical in industries like healthcare or finance, where compliance with privacy regulations is non-negotiable.
The key to addressing security concerns is to ensure that your integration strategy includes strong data encryption, secure APIs, and regular security audits. Additionally, ensuring compliance with industry-specific regulations, like HIPAA in healthcare, is vital. By making security a priority from the outset, you can reduce the risk of breaches while still enjoying the benefits of integration.
Resistance to Change
Even if you have the best technology and processes in place, one of the biggest challenges can still be resistance from your own team. Employees are often reluctant to adopt new systems, especially if they’re used to working a certain way. This resistance can slow down the integration process and prevent your business from reaping its full benefits.
So how do you overcome this? Leadership plays a crucial role in driving integration success. When executives champion the integration process and clearly communicate its benefits, employees are more likely to get on board. Additionally, investing in user-friendly platforms and providing comprehensive employee training can help ease the transition. By supporting your team throughout the process, you can foster a culture of collaboration and ensure that everyone is aligned with the integration goals.
Ensuring Post-Integration Success
Once you’ve overcome the initial challenges of integration, it’s important to remember that the process doesn’t end there. Continuous monitoring and improvement are key to maintaining a smooth, efficient system. Regularly reviewing system performance, identifying any new bottlenecks, and staying up-to-date on the latest integration technologies can help you keep everything running smoothly.
One effective approach is to establish a dedicated team responsible for overseeing the integration’s long-term success. This team can monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), address any emerging issues, and recommend improvements as your business evolves. By keeping integration top of mind, you’ll ensure that it continues to deliver value for years to come.
At the end of the day, successful integration is about more than just uniting systems—it’s about creating a connected, collaborative organization that can adapt to future challenges and opportunities.
And that’s the beauty of seamless process integration: it’s not just a one-time project—it’s a continuous journey of improvement!
Until next time,